Problem:
What is the difference between “off delay” and “true off delay” time delay relays, and when to use the true off delay function?
Solution/Resolution:
Pneumatic time delay relays work well, but they are usually very large and very expensive. In addition, they only have two functions available: normal open time close (N.O.T.C.) and normal close time open (N.C.T.O.) contact delay; and normally open time open (N.O.T.O.) and normally closed time close (N.C.T.C.) contact delay.
Sometime in the 1970s, manufacturers developed solid-state time delay relays, initially using some type of RC (resistance-capacitor) circuit to set the time delay. Now most of them use integrated circuits or microprocessors to realize functions and time delays.
One disadvantage of solid-state time delay relays is the attempt to replace the Off delay pneumatic unit. The old pneumatic unit does not need to maintain the input voltage during the shutdown delay: when the input voltage is applied to the pneumatic delay unit, the voltage of the contact change country is removed, and the contact is still changing state until the air passes from a room to The other, thereby completing the time delay and changing the contact back to normal state.
A solid-state Off Delay product requires a continuous input voltage during the Off Delay period so the logic circuits and output relays both remain energized. Otherwise, when the input voltage is removed, the relays will be left grounded.the relay will exit immediately instead of completing the OFF delay.
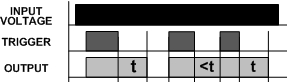
Turn off delay function operation
After the input voltage is applied, the delay relay is ready to accept the trigger. When the trigger is applied, the output is activated. After the trigger is removed, the time delay (t) begins. A delay of time (t) is followed by de-energizing the output.During the delay, any application of the flip-flop will reset the delay (t), and the output remains energized.
In order to solve this problem, the manufacturer has proposed a unit commonly referred to as “true off delay”. In these products, logic circuits and relays are kept energized by the on-board power supply. This can be a capacitor that is discharged during the off delay to keep the logic and output relays energized. Or it may be a latching relay that keeps the latch closed during the off delay, and then a small capacitor discharges during the off delay to release the latch. Use of a small battery is another option.
In all cases, the idea is to make the unit have its own power supply as a shutdown delay, rather than an external power supply like the standard shutdown delay solid state unit.
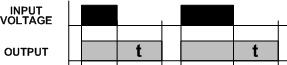
True-Off Delay function operation
After the input voltage is applied, the output is energized. When the input voltage is removed, the time delay (t) starts. A delay of time (t) is followed by de-energizing the output.The input voltage must be applied for at least 0.1 seconds to ensure normal operation. The time delay (t) will be reset by applying input voltage during the delay period (t).No external trigger is required.
There is also a version called delayed on/off delay. Here is how it works:
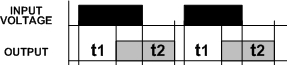
Delay on/off delay function operation
After the input voltage is applied, the time delay (t1) starts. An output is energized following the time delay (t1). When the input voltage is removed, the output remains energized during the delay (t2). At the end of the delay (t2), the output is de-energized. The input voltage must be applied for at least 0.1 seconds to ensure normal operation. During the delay (t2) any effect of the input voltage will keep the output energized and reset the delay (t2). No external trigger is required.
Therefore, for replacing old pneumatic time delay relays or applications where the input voltage is not available during the off delay, the true off delay function is perfect.